React Support
Using Create React App
You can use Create React App to create a project from template. Note that you need to use the cra-template-cohtml package and react-scripts-cohtml.
- Install Create React App:
npm i -g create-react-app
You can use npx, for more information follow this guide.
- Then run:
create-react-app my-app --scripts-version react-scripts-cohtml --template cra-template-cohtml
This will create a React application using special configuration defined in react-scripts-cohtml and the custom template for Prysm.
- Navigate to the newly created application using
cd my-app
and run
npm start
to start a development server with live reload.
For the full list of the available commands refer to the documentation.
How to open the Player when you are running a dev server
To have the Player open when you run the dev server, you will need to provide the path to the Player.exe file in the .env file.
In the .env file you need to add the PLAYER_PATH variable whose value should be the absolute or relative path to the Player.exe file.
For example:
PLAYER_PATH = '../../../Player/Player.exe'
Since the default behavior of the template is to open the Player, you can disable it by adding NO_PLAYER=true to the .env file
How to change the build folder
By default whenever you are building a React project the default output folder will be ./build. If you want to change that so that the source and the built files are kept separately, add the following to the .env file:
BUILD_PATH={{PATH TO BUILD FOLDER}}
PUBLIC_URL='./'
Unity3D project
There is an automatic way to set up a new project in development configuration by pressing the Prysm/Setup a development React App button in the Context Menu. This will create a React application ready to work within the Unity3D project. It will also start the development server automatically on http://localhost:[port]., where [port] is the port provided by React.
To create a React app manually and configure it to work in a Unity3D project for Development and Production configuration, set up the Create React App in any location except in the Assets folder in the Unity3D project.
Development configuration
- In the
[Unity3DProjectDir]/my-app/.envfile add:
NO_PLAYER=true
This will prevent a possible PLAYER_PATH environment variable not set error.
- Go to
[Unity3DProjectDir]/my-app/and executenpm start. - Assign the Page URL field of the
CohtmlViewcomponent tohttp://localhost:[port].
Production configuration
- In the
[Unity3DProjectDir]/my-app/.envfile and add the following line:
BUILD_PATH="../Assets/StreamingAssets/Cohtml/UIResources/Build"
PUBLIC_URL="./"
BUILD_PATH will deploy the files to UIResources/Build folder from where the Unity3D integration can load the HTML pages. PUBLIC_URL will resolve the resource paths to be loaded locally.
- In
[Unity3DProjectDir]/my-app/executenpm run buildto build the in production mode. - In the
CohtmlViewcomponent in the scene, in the Page URL field set tocoui://UIResources/Build/index.html.
Creating a React Toolchain
You can create a custom React toolchain using Webpack and Babel. The custom toolchain provides more flexibility.
To set up a development server with HMR (hot-module-replacement), use webpack-dev-server. Babel is required to handle the export/import module and the jsx syntax. To build or serve the application files, use Webpack.
To handle styles use mini-css-extract-plugin and css-loader. You can use Sass and Less loaders to handle Sass and Less respectively. To handle HTML files use html-webpack-plugin. To enable HRM (hot-module-replacement), use react-hot-loader.
Setup a Toolchain
Use npm or the package manager of your choice to initialize the project, set up scripts, and install and manage dependencies.
1. Project Initialization
To initialize your project, create a new folder and run npm init. Once you have completed the project initialization, add the dependencies and devDependencies to the package.json file.
"devDependencies": {
"@babel/core": "7.21.3",
"@babel/plugin-syntax-jsx": "7.18.6",
"@babel/plugin-transform-runtime": "7.21.0",
"@babel/preset-env": "7.20.2",
"@babel/preset-react": "7.18.6",
"babel-loader": "9.1.2",
"css-loader": "6.7.3",
"extract-loader": "5.1.0",
"file-loader": "6.2.0",
"html-loader": "4.2.0",
"html-webpack-plugin": "5.5.0",
"mini-css-extract-plugin": "2.7.5",
"style-loader": "3.3.2",
"webpack": "5.76.3",
"webpack-cli": "5.0.1",
"webpack-dev-server": "4.13.1",
"postmessage-polyfill": "1.0.0",
"whatwg-fetch": "3.6.2"
}
"dependencies": {
"react": "18.2.0",
"react-dom": "18.2.0"
}
2. Setup Scripts
Add the following npm scripts:
"scripts": {
"build": "webpack --env production",
"build:dev": "webpack --env development",
"watch": "webpack serve"
},
3. Webpack Plugins
Create the webpack.config.js file in the same directory as the package.json and open it in your text editor of choice. Include the following webpack plugins at the top of the webpack.config.js file.
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
const MiniCssExtractPlugin = require('mini-css-extract-plugin');
You should also import webpack and the NodeJS path module:
const path = require('path');
const webpack = require('webpack');
You can export a function from the webpack.config.js file using module.exports = function (env) {}.
4. Define Webpack Build Mode:
const isProd = env.production === true;
5. Specify an Entry for Webpack
The entry tells Webpack where to start bundling.
Add this at the top of the webpack.config.js file.
const entry = [path.resolve(__dirname) + "<path_to_entry>"];
Create the config object and set the entry, output, devtool and plugins properties. The output specifies the directory in which bundled files will be saved, as well as their names.
const config = {
entry: entry,
devtool: false,
plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: './src/index.html',
filename: './index.html'
}),
new MiniCssExtractPlugin()
]
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, "dist/"),
publicPath: "./",
filename: "bundle.js",
assetModuleFilename: '[name][ext]'
},
},
6. Module Rules
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.js$/,
exclude: /(node_modules)/,
use: {
loader: 'babel-loader',
options: {
presets: ['@babel/preset-env', '@babel/preset-react'],
plugins: ['@babel/plugin-transform-runtime', '@babel/plugin-syntax-jsx']
}
}
},
{
test: /\.css$/,
use: [MiniCssExtractPlugin.loader, 'css-loader']
},
{
test: /\.(jpe?g|png|gif|svg)$/i,
type: 'asset/resource'
}
]
},
To handle ES6+ and JSX syntax, use babel-loader along with @babel/env and @babel/preset-react presets.
To serve the files to a development server with HMR and automatic watch, add configuration for development server only if the environment is not production:
if (!isProd) {
config.devServer = {
allowedHosts: 'all',
static: path.join(__dirname, 'src/'),
port: 9000,
hot: true,
compress: true,
};
config.watchOptions = {
poll: 2000,
aggregateTimeout: 600,
}
config.output = {
publicPath: 'http://localhost:9000/',
}
config.entry.push('webpack/hot/poll?2000');
}
The poll entry is added to enable watch using polling.
To change the poll interval, change the value of the poll property in the watchOptions object. Use the static property to specify the path of the source.
And finally, you need to return the config object:
return config;
};
Create a Sample Using the Toolchain from the Previous Section
There is a complete sample in <package>\Samples\uiresources\React.
Create a src folder and add components and images folders inside it. Create an index.html file inside that folder:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>React Starter</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
</html>
Create an index.js inside the same src folder.
import React from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom/client";
import App from "./components/app/app.js";
// cohtml.js exports an UMD module, because of Babel you can use
// import statement to include it in the bundle and the global engine
// variable will be automatically initialized
import '../cohtml.js';
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById("root"));
root.render(<App />);
Get cohtml.js from <package>\Samples\uiresources\library.
The index.html is the starting point of the React app. The application is rendered inside the "#root" element in the HTML.
Import the components needed for the initial load of the app and render them in the "#root" element. Put the images that are going to be used inside the images folder, then create an app, potion and potions folders inside the components folder.
Inside the app folder create app.css and app.js files:
import React, { Component } from "react";
import "./app.css";
import Potions from '../potions';
import Inventory_Frame from '../../images/Inventory_Frame.png';
import Inventory_HealthPotion from '../../images/Inventory_HealthPotion.png';
import InventoryPoisonPotion from '../../images/InventoryPoisonPotion.png';
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div id="app">
<Potions></Potions>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;
Add the code below to the index.js file in the potions folder:
import React, {h, render, Component } from 'react';
import Potion from '../potion';
class Potions extends Component {
constructor(props) { super(props); }
render() {
return (
<div>
<div id="potion_bar"></div>
<Potion
value="5"
id="health_potion_value"
className="potion"
imageid="health_potion"
imageClassName="health-potion-animation health-potion-image"></Potion>
<Potion
value="70"
id="energy_potion_value"
className="potion"
imageid="energy_potion"
imageClassName="energy-potion-animation energy-potion-image"></Potion>
</div>
)
}
}
export default Potions;
Create a container for the health and energy potions by adding this code to the index.js file inside the potion folder.
import React from 'react';
import { h, render, Component } from 'react';
class Potion extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
value: props.value || 50,
};
}
onUse() {
if(!this.state.value) return;
this.setState({
value: this.state.value-1
});
}
render() {
return (
<div className="pointer-cursor">
<div id={this.props.imageid} className={this.props.imageClassName} onClick={() => {this.onUse();}}></div>
<div id={this.props.id} className={this.props.className}>{ this.state.value }</div>
</div>
);
}
}
export default Potion;
The potions component is a “stateful” component that remembers the number of potions that haven’t been used yet. It also attaches onClickHandlers.
- Run
npm installin the root of the sample - Run:
npm run buildfor a minified production buildnpm run build:devfor a development buildnpm run watchto start a development server with hot module replacement
Make sure to add this polyfill in development mode in src/index.js:
import {pm} from 'postmessage-polyfill';
import {fetch as fetchPolyfill} from 'whatwg-fetch';
window.postMessage = function(message) {
pm({
type: message.type,
origin: 'http://127.0.0.1/:9000',
target: window,
data: message.data
});
};
There’s no need to manually install whatwg-fetch and postmessage-polyfill because they are to the devDependencies of the sample.
HMR (Hot Module Replacement)
Hot Module Replacement is already enabled in step 6 from the previous section by setting hot: true for the devServer object.
React Redux v8.0.5
Prysm supports react-redux. Redux is a predictable state container for JavaScript applications. React-redux is the redux package for react.js.
You should use react-redux in Prysm just as you would use it in a web browser. The following example creates a simple counter, using react-redux.
A similar Counter app with a working environment can be found here.
- First, create the reducer which will describe how the state should change when an action is received.
export default (state = 0, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'INCREMENT':
return state + 1
case 'DECREMENT':
return state - 1
default:
return state
}
}
- Next create the Counter component, which displays the buttons for increment and decrement.
class Counter extends Component {
render() {
const { value, onIncrement, onDecrement } = this.props
return (
<div className="counter-container">
Clicked: {value} times
<div className="button" onClick={onIncrement}>+</div>
<div className="button" onClick={onDecrement}>-</div>
</div>
)
}
}
- After that create the entry file - index.js.
// create the store
const store = createStore(counter);
const rootEl = document.getElementById('root');
const render = () => ReactDOM.render(
<Counter
value={store.getState()}
onIncrement={() => store.dispatch({ type: 'INCREMENT' })}
onDecrement={() => store.dispatch({ type: 'DECREMENT' })}
/>,
rootEl
);
// render the Counter component into the DOM
render();
// subscribe for a change in the store
store.subscribe(render);
The folder structure should look like this:

Reference Sample
This sample works in Gameface 1.39.0.2 and the Counter app is created using this package.json.
React v18.2.0 and React Redux v8.0.5 are used in this sample.
Debugging
You can use React Developer Tools to inspect a React application in Prysm. The tools provide an inspector that reveals the React components tree that builds your page, and for each component, you can go and check the props, the state, hooks, etc.
Prysm supports the standalone version of the React Development Tools version 4.27.6. It is available as an npm package. You can install it by typing the following command in a console:
npm install -g react-devtools
You can check the package here.
To start debugging you need to add the following script as the first script tag in the <head> of your page:
<script src="http://localhost:8097"></script>
The port might be different. When you launch react-devtools you will be presented with information about the port the server is listening on.
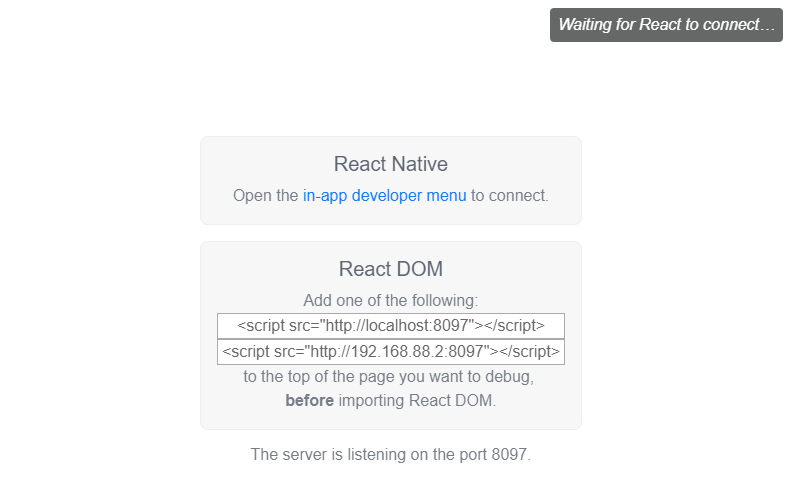
To launch React Developer Tools type this in a terminal:
react-devtools
It will automatically connect to the page as long as it is open and it has the required <script> tag.
Here you can find various guides and articles on how to use React Devtools.
Styling Components
You can use CSS Modules to style your React components. The CSS Modules enable you to write CSS rules that can be applied to many elements using the same name, but during the build, the CSS loader will scope the names locally using the component name. For example, a file that contains a class name hidden can be used in the component modal, in the component dropdown, and the CSS loader will automatically generate class names modal_hidden and dropdown_hidden respectively for each component. The naming convention is more complicated to ensure that there are no duplications, but this is a high-level overview of how CSS modules work.
In order to use CSS modules, you need to configure Webpack to use the correct loaders. Replace the .css rule with the following configuration in webpack.config.js:
const MiniCssExtractPlugin = require("mini-css-extract-plugin");
...
{
test: /\.css$/,
use: [
MiniCssExtractPlugin.loader,
{
loader: "css-loader",
options: {
modules: {
localIdentName: '[name]__[local]___[hash:hex:5]'
}
},
}]
}
The most important change is the options that we added to the css-loader. The module’s object specifies that CSS modules are enabled. The localIdentName specifies the name of the generated scoped CSS rule.
After Webpack is configured, import a style in a component like this:
import styles from '../style.css';
Example style.css content:
.btn {
width: 100px;
background-color: aquamarine;
height: 5vw;
margin: 2vw;
border: none;
position: absolute;
right: 0px;
top: auto;
left: auto;
}
And then use it like this:
btn.js:
render() {
return (
<div>
<button className={styles.btn}>Click Me</button>
</div>
);
}
Note: If a dash-separated class name is used, the usage is className={styles["btn-large"]}.
The generated HTML from this usage will be:
<button class="btn__btn___1Aigk">Click Me</button>
And if you use the same class from the same file in another component the name will be different.
Please note, that React-JSS, styled-components and CSS modules in create-react-app are not supported.